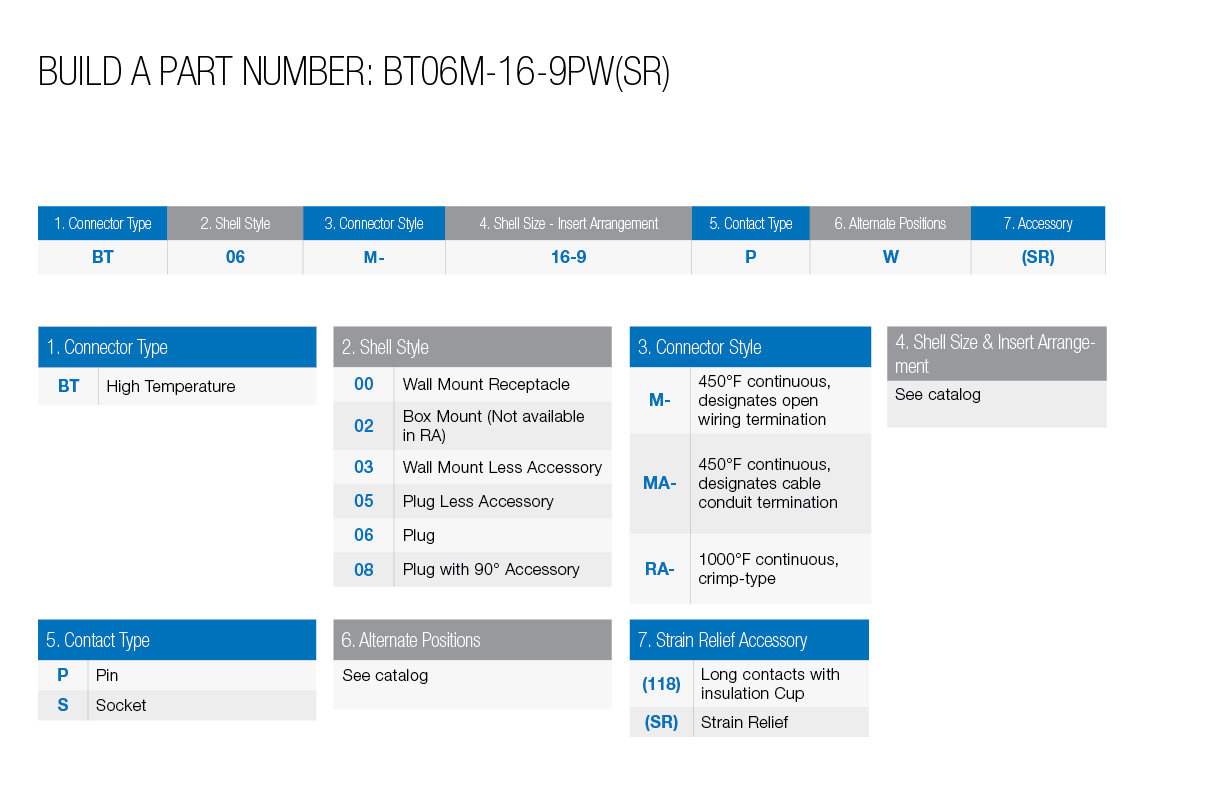
BT High Temperature Connectors

Contact:
Description:
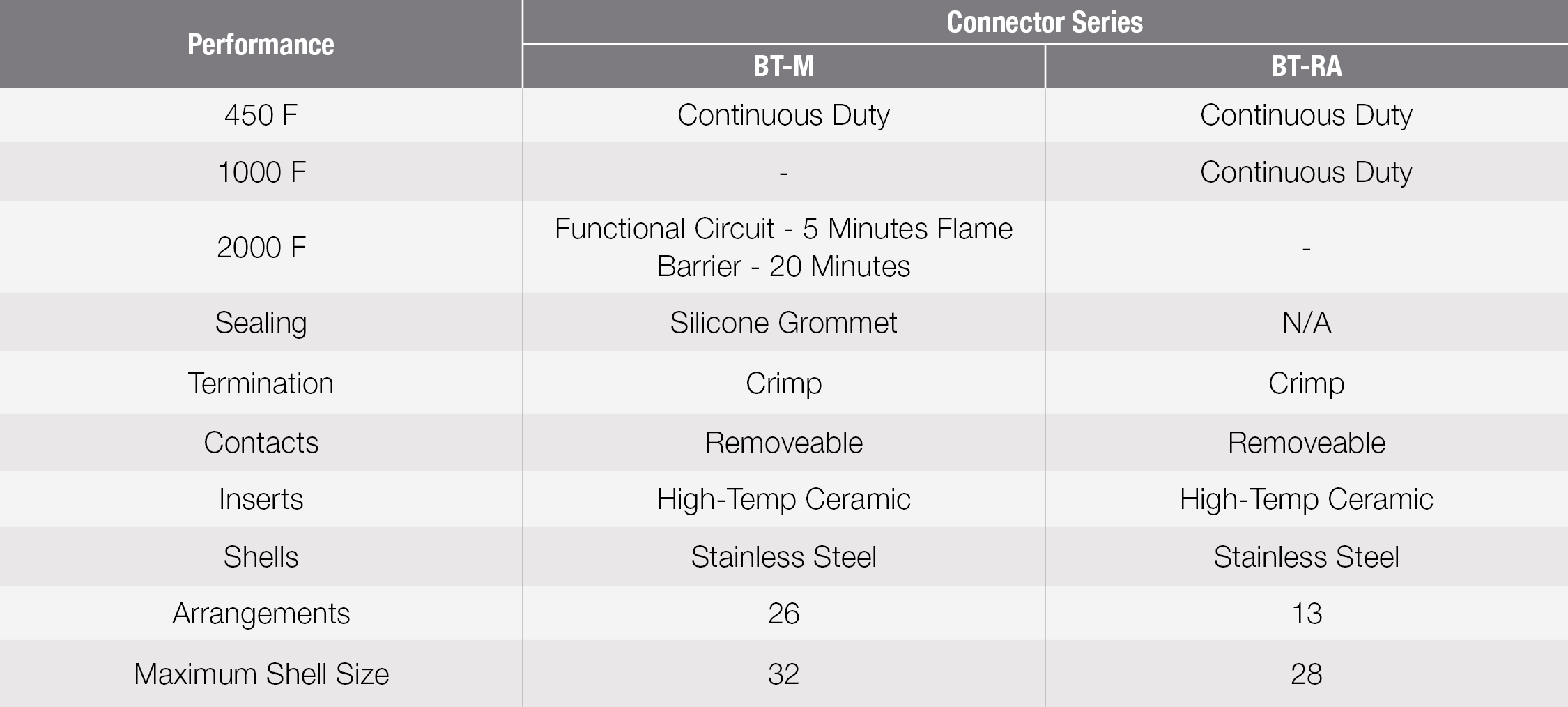
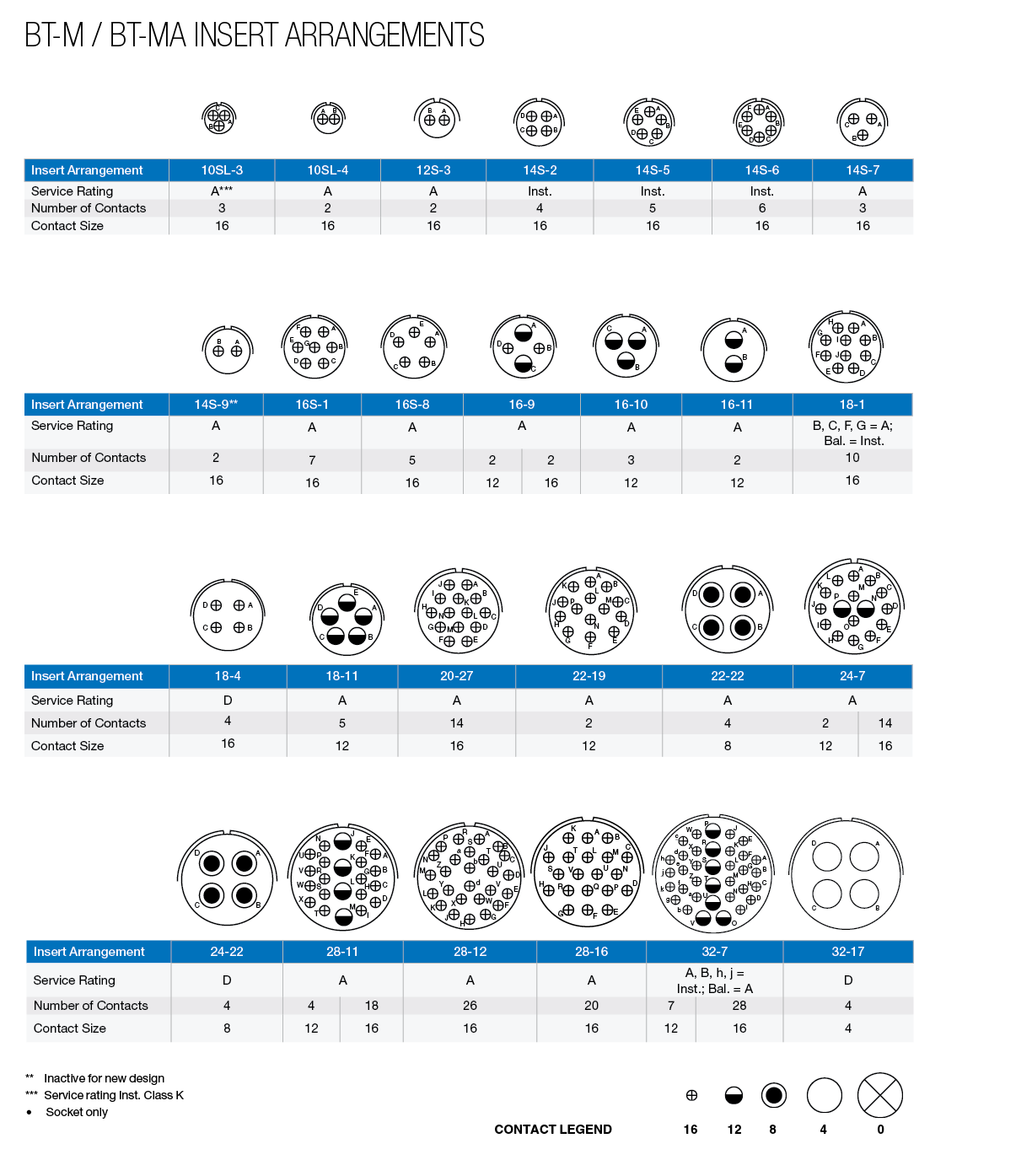
BT-M Connectors:
BT-M firewall electrical connectors were specially designed for service where high-temperature performance and direct exposure to flame are prevalent.
It is important to note that the BT-M series is divided into two categories. The first category, BT-M, utilizes a MS-R type silicone grommet and clamp for termination of open wiring. The second category, the BT-MA, utilizes a conduit adapter for termination of cable conduit.
The BT-M series connector will maintain a functional circuit under extreme heat of 2000°F (1093°C) for 5 minutes. It will also sustain a flame barrier for an additional 15 minutes. Continuous duty at an elevated temperature up to 450°F (232°C) is assured
BT-RA Connectors:
BT-RA connectors meet the applicable requirements of Class A connectors to MIL-C-5015D and will operate continuously at temperatures up to 1000°F (537°C). Intermateability and interchangeability with MIL-C-5015 connectors is assured. This connector series features rear removable crimp type contacts to ease assembly procedures and provides very little change in millivolt drop (contact resistance) during and after exposure to high-temperature and vibration.
Features & Benefits:
BT-M:
- Stainless steel shells provide added durability and resistance to corrosion.
- High density alumina oxide/silicone inserts provide increased performance in the following characteristics:
- High resistance to vibration damage
- Durability
- Overall connector reliability
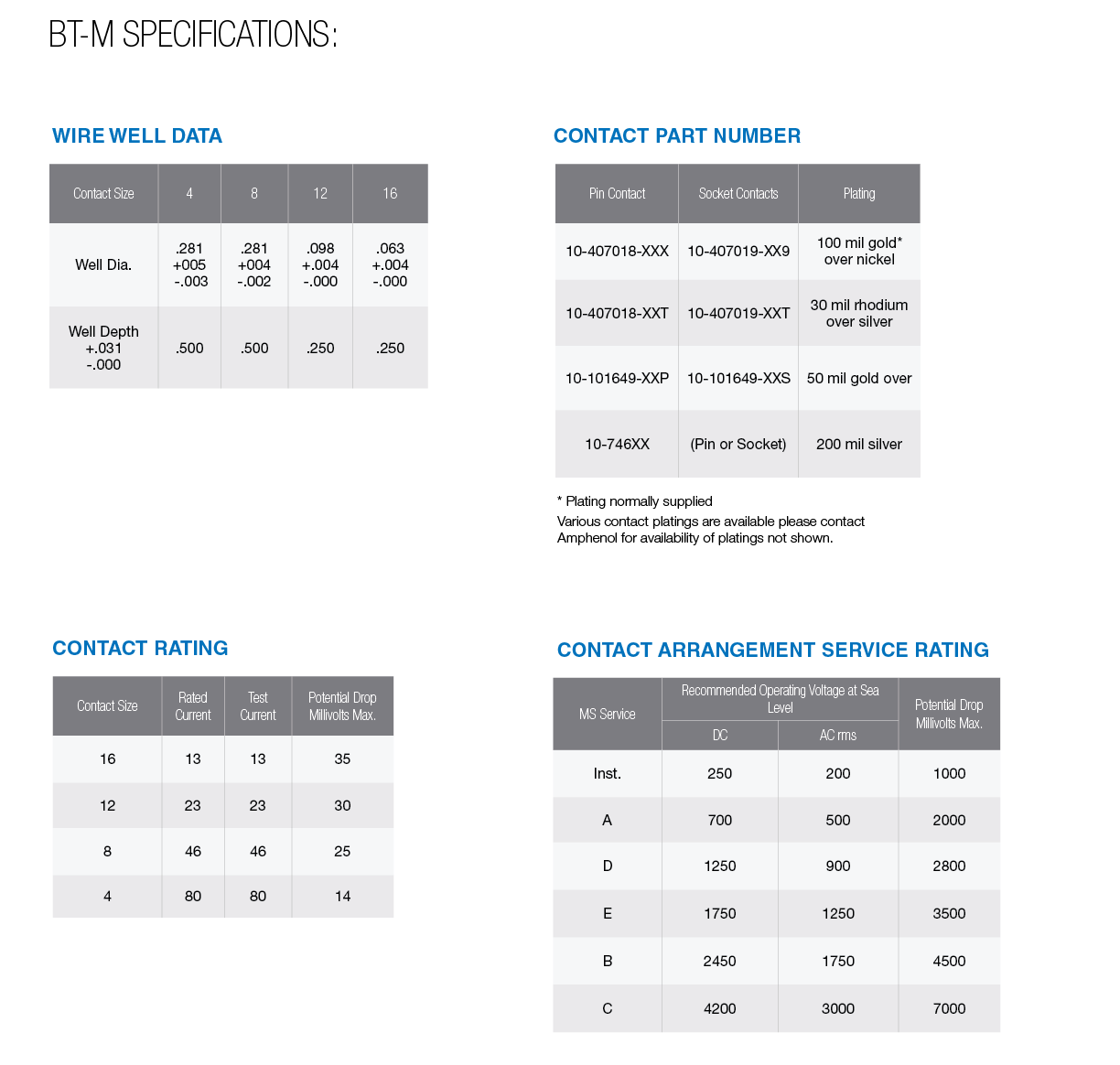
- Crimp-type, gold plated contacts designed for use with wire conforming to MIL-W-5086 requirements.
BT-RA:
- Shells and coupling nuts are fabricated from stainless steel to provide durability and resistance to corrosion and high-temperatures.
- Contacts are machined from nickel and are heavy gold plated for excellent electrical properties at high-temperatures.
- Inserts are ceramic moldings and contain spring clips for retaining contacts. This combination of materials and plating also provides resistance to radiation and oxidation.